TASK 1
Tittle : I' m Fine Thanks
Directed : Eamonn O'neill
Produced : Royal College of Art Made in UK.
Video : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QSdi9Gi1to4
Award : Best Graduate Film - Ottawa International Animation Festival 2011.
Best Animation - Darklight Film Festival 2011.
Synopsis : He has bullied with a girl and don't know read the book. And then, no one girl love him. Lastly, he has suffered from depression.
What is Animation
Animation is the process of displaying still images in a rapid sequence to create the illusion of movement. These images can be hand drawn, computer generated, or pictures of 3D objects.
History about Animation
Early animations, which started appearing before 1910, consisted of simple drawings photographed one at a time. It was extremely labor intensive as there were literally hundreds of drawings per minute of film. The development of celluloid around 1913 quickly made animation easier to manage.
How many type of Animation
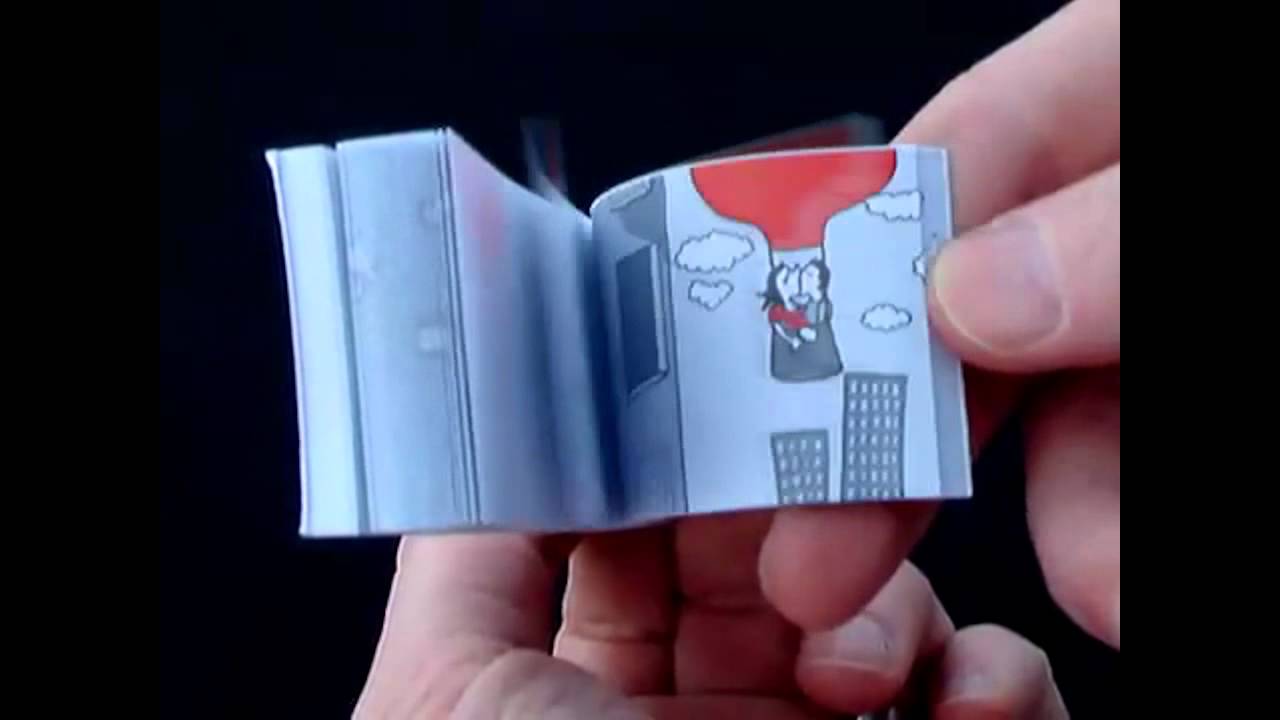
1. Flip book
A flip book or flick book is a book with a series of pictures that vary gradually from one page to the next, so that when the pages are turned rapidly, the pictures appear to animate by simulating motion or some other change. Flip books are often illustrated books for children, but may also be geared towards adults and employ a series of photographs rather than drawings.
2. Stop motion
Stop motion is animation makes use of figurine and physical objects to create animation. You can start with using toys and potable figurine and capture them as photo images. Posing the toys frame by frame and the animation will look relatively appealing if you are using toys because they look real life.
Type of Stop motion:
- Cutout animation
- Clay animation/ claymation

- Object animation

- Puppet animation

3. Computer Animation
computer graphics and animation technologies. It is the creation of moving images (animation) using computer technology. Usually create 3D and 2D animation
- 3D animation
- 2D animation
2D animation creates movement in a two-dimensional artistic space. Work in the field of 2D animation requires both creativity and technological skills.

What
is the tool used for animation.
1.
Anime
Studio
2. Digicel flipbook
DigiCel FlipBook lets you draw right on the computer with your mouse or tablet. Or you can draw on paper, like the pros, and shoot your rough drawings under a camera for speed and then scan your cleaned-up drawings for quality. FlipBook will keep track of all your drawings in its traditional exposure sheet with thumbnail images and play them back instantly with sound.
3. CreaToon
CreaToon allows you to do cut-out-shape animation without having to set every single frame. Just set certain keyframes and the computer will do the in-betweens. Thanks to the real-time preview and the keyframe editor, you can easily fine-tune your animation until you are satisfied with the result.
4. Toon Boom Studio
Toon Boom is a simple-to-use animation software for producing online content. Create animation with a variety of drawing tools. Import and animate media elements such as digital pictures and capture live images. Connect a character to simple-to-use bone animation tools.
8. Wideo
DigiCel FlipBook lets you draw right on the computer with your mouse or tablet. Or you can draw on paper, like the pros, and shoot your rough drawings under a camera for speed and then scan your cleaned-up drawings for quality. FlipBook will keep track of all your drawings in its traditional exposure sheet with thumbnail images and play them back instantly with sound.
CreaToon allows you to do cut-out-shape animation without having to set every single frame. Just set certain keyframes and the computer will do the in-betweens. Thanks to the real-time preview and the keyframe editor, you can easily fine-tune your animation until you are satisfied with the result.
Toon Boom is a simple-to-use animation software for producing online content. Create animation with a variety of drawing tools. Import and animate media elements such as digital pictures and capture live images. Connect a character to simple-to-use bone animation tools.
5. FotoMorph
FotoMorph is one of the rare programs that manage to deliver impressive results with very little know-how. This fun application lets users create animations that morph one photo into another, no experience required. The program's interface is attractive and intuitive.
6. Pencil
Pencil2D is a free and open-source 2D animation software available for Windows, Mac OS, and Linux. It is a fork of Pencil. The application uses a bitmap/vector drawing interface to produce simple 2D graphics as well as animation.
7. GoAnimate
GoAnimate is a cloud-based platform for creating and distributing animated videos. It allows users to develop both narrative videos, in which characters speak with lip-sync and move around, and video presentations, in which a voice-over narrator speaks over images and props, which may also move around.
8. Wideo
Wideo is an animated online video creation platform that allows you to create, edit, and share videos online for free. You can choose (or upload) images, backgrounds, and music that you want to use in order to create your own online video and then share it with the world.
9. Synfig Studio
Synfig Studio (also known as Synfig) is a free and open source 2D vector graphics and timeline-based computer animation program created by Robert Quattlebaum with additional contributions by Adrian Bentley.
10. Blender
Blender is a professional free and open-source 3D computer graphics software product used for creating animated films, visual effects, art, 3D printed models, interactive 3D applications and video games. Blender's features include 3D modeling.
11. TVPaint Animation
TVPaint Animation is a paperless drawing and animation tool, able to imitate traditional techniques such as pen brush, watercolor, pencil, felt-tip and airbrush, and animate them over frames. TVPaint Animation (also known as TVPaint, TVP Animation, Mirage and Newtek Aura) is a 2D, bitmap-based digital animation software package, developed and distributed by TVPaint Developpement, France.
12. Anim8or
Anim8or is a 3D computer animation program that is designed to allow straightforward creation of animations. This is a good introductory program to 3D animating. It is can render high quality .jpg and .bmp images and movies.
13. Xtranormal.
Xtranormal is an online application to make 3D animated videos. Choose from 500 high-quality actors and 200 beautiful sets. Insert up to 12 actors per scene. Technology, Inc. is a digital entertainment company that formerly produced do-it-yourself animation software for the web and desktop and turned words from a script into an animated movie using text-to-speech and animation technologies.
14. Muvizu
Muvizu is a fun and easy to use 3D. Create and customize 3D characters, virtual lights, cameras and special effects, automatic lip-synching for any language, lightning fast rendering for quick results. Bring the whole performance to life with our awesome character animation system. Create and customize 3D characters.
15. Art of Illusion.
Art of Illusion is a software package used for 3D modeling, texturing, ray tracing, and otherwise rendering computer generated imagery stills or animations (movies). Art of Illusion is capable of modeling and rendering photorealistic images and animations; it is also capable of non-photorealistic rendering as well.
16. Adobe After Effects
Adobe After Effects is a digital visual effects, motion graphics, and compositing application developed by Adobe Systems and used in the post-production process of filmmaking and television production. Among other things, After Effects can be used for keying, tracking, rot scoping, compositing and animation.
17. Sweet Home 3D
Sweet Home 3D is a free architectural design software application that helps users create a 2D plan of a house, with a 3D preview, and decorate exterior and interior view including ability to place furniture and home appliance. In Sweet Home 3D, furniture can be imported and arranged to create a virtual environment.
18. SketchUp
SketchUp (formerly: Google Sketchup) is a 3D modeling computer program for applications such as architectural, interior design, civil and mechanical engineering, film, and video game design. A freeware version, SketchUp Make, and a paid version with additional functionality, SketchUp Pro, are available.
19. Lightwave
LightWave 3D is a 3D computer graphics software developed by NewTek. It has been used in film, television, motion graphics, digital matte painting, visual effects, video games development, product design, architectural visualizations, virtual production, music videos, pre-visualizations and advertising.
20. Adobe Flash
Adobe Flash (formerly called Macromedia Flash and Shockwave Flash) is a multimedia and software platform used for creating vector graphics, animation, games and rich Internet applications (RIAs) that can be viewed, played and executed in Adobe Flash Player.
12 Principles of Animation.
The following 12 basic principles of animation were developed by the ‘old men’ of Walt Disney Studios, amongst them Frank Thomas and Ollie Johnston, during the 1930s. These principles came as a result of reflection about their practice and through Disney’s desire to devise a way animating that seemed more ‘real’ in terms of how things moved, and how that movement might be used to express character and personality. John Lasseter, “ Principles of Traditional Animation Applied to 3D Computer Animation ”,
1. Solid drawing
In 2D animation, solid drawing is about creating an accurate drawing with volume and weight, and thinking about balance, and the anatomy in a pose. With 3D animation animators are less likely to rely on their drawings, but the idea of solid drawing is just as important. With solid drawing you need to think about how you pose out your 3D characters rig, ensuring there is correct balance and weight.
2. Timing and Spacing.
Timing and spacing in animation is what gives objects and characters the illusion of moving within the laws of physics. Timing refers to the number of frames between two poses.
3. Squash and Stretch.
Squash and Stretch is what gives flexibility to objects. There’s a lot of squash and stretch happening in real life. In animation this can be exaggerated.. Squash and stretch can be implemented in many different. Like the eyes during a blink or when someone gets surprised or scared their face squashes down. Squash and stretch is a great principle to exaggerate animations and more appeal to a movement.
4. Anticipation
Anticipation is used in animation to set the audience up for an action that is about to happen. Example if a person needs to move back slightly, this not only get their momentum up. But it also lets the audience know this person is about to move.
5. Ease In Ease Out
As any object or person moves or comes to a stop there needs to be a time for acceleration and deceleration. Without ease in and ease out (or slow in slow out), movements become very unnatural and robotic. As a character stands up from a sitting position the spacing will be closer together at the start, so they ease into the movement, and as they stand up, they will ease out of the movement.
6. Arcs
Everything in real-life typically moves in some type of arcing motion, and in animation you should adhere to this principle of arcs to ensure your animation is smooth and moves in a realistic way. The only time something would move in a perfectly straight line is if you’re trying to animate a robot, because it’s unnatural for people to move in straight lines. For example, if a character is turning their head, they will dip their head down during the turn creating an arcing motion. You also want to ensure the more subtle things move in arcs as well, for example the tips of the toes should move in rounded arcing motions as the character walks.
7. Secondary Action
Secondary action refers to creating actions that emphasize or support the main action of the animation; it can breathe more life into an animation and create a more convincing performance. It’s important to remember that the secondary action should typically be something subtle that doesn’t detract from the main action happening, and can be thought of as almost a subconscious action.
8. Follow Through and Overlapping Action
Follow through and overlapping action can be considered two different principles, but they’re still closely related. Follow through is the idea that separate parts of the body will continue moving after the character has come to a stop. For example, as a character comes to a stop from a walk, every part of the body won’t stop at the exact same time, instead, the arms may continue forward before coming to a settle. Overlapping action is very similar in that it means different parts of the body will move at different times. For example, if a character raises their arm up to wave, the shoulder will move first, and then the arm, and the elbow and hand may lag behind a few frames.
9. Straight Ahead and Pose to Pose
Straight ahead and pose to pose refers to the two different techniques for how you go about animating. With straight ahead it’s a very spontaneous and more of a linear approach. You’ll create each pose or drawing of the animation one after the other. For example, if you’re animating a character jumping in the air you would create the pose where he’s standing, the next where he is beginning to kneel down, the next would be him completely crouched, and so on.
10. Staging
characters so that both of them are easily viewed from Staging is how you go about setting up your scene, from the placement of the characters to the background and foreground elements and how the camera angle is set up. The purpose of staging is to make the purpose of the animation unmistakably clear to the viewer.
11. Appeal
This principle can really come down to adding more appeal in many different areas of your animation, such as appeal in posing. You can find areas on the character to push and exaggerate to create a more unique character design that will stick out in the audience’s memory.
12. Exaggeration
Exaggeration is used to push movements further to add more appeal to an action. Exaggeration can be used to create extremely cartoony movements, or incorporated with a little more restrain to more realistic actions. If you have a realistic animation you can use exaggeration to make a more readable or fun movement while staying true to reality.
Ollie Johnston and Frank Thomas Biography
Oliver Martin "Ollie" Johnston, Jr. (October 31, 1912 – April 14, 2008) was an American motion picture animator. He was one of Disney's Nine Old Men, and the last surviving at the time of his death from natural causes. He was recognized by The Walt Disney Company with its Disney Legend Award in 1989. His work was recognized with the National Medal of Arts in 2005. He was an animator at Walt Disney Studios from 1935 to 1978, and became a directing animator.
Franklin Rosborough “Frank” Thomas (September 5, 1912 – September 8, 2004) was an American animator. He was one of Walt Disney’s team of animators; known as the Nine Old Me. He born in Fresno, California,
Type of face
Type of eyes
Type of nose
Type of mouth
Type of hair
Type of hand
Type of shirt
Type of pants
Type of shoes
Character sketches
Main Character
Hand movement
Body movement





















































No comments:
Post a Comment